Cleaning up XP Junk with batch file
Clean up your system TEMP, RECENT, HISTORY, TEMPRORY INTERNET FILES, & PREFETCH files Via a simple Batch File
Copy this code to Notepad And save it as Cleanup.bat
Please Note: ALWAYS RUN THIS FILE FROM SYSTEM DESKTOP
@echo Off
@Title Ghost Nt Cleaning System File
@
@cd\
@
Echo. Cleaning Prefetch Files
@cd %windir%\prefetch
@del /s /q *.* echo. >nul
@cd\
Echo. Cleaning Temporary Files
@cd %USERPROFILE%\Local Settings\Temporary Internet Files
@del /f /s /q /a s *.* echo. >nul
@cd..
@rd /s /q Temp echo. >nul
@rd /s /q History echo. >nul
@
@MD Temp
@cd\
@del /s /q *.tmp
@
@cd %USERPROFILE%\Recent
@del /s /q *.* echo. >nul
Echo. Please Wait More For Last Cleanup
@del /s /q *.chk echo. >nul
@
Echo. Cleanup Sucessfull
Hope this helps
Wednesday, July 9, 2008
Need not Re-Activate Windows XP after Re-Installation
Need not Re-Activate Windows XP after Re-Installation
If you have to reinstall Windows XP you normally will have to reactivate too. Well not anymore. Just copy wpa.dbl after you activated the first time. It is located in the WINDOWS\system32 folder. Now if you reinstall Windows XP just copy the file back and you're up and running again.
If you have to reinstall Windows XP you normally will have to reactivate too. Well not anymore. Just copy wpa.dbl after you activated the first time. It is located in the WINDOWS\system32 folder. Now if you reinstall Windows XP just copy the file back and you're up and running again.
Tuesday, July 8, 2008
Speeding Up Vista Boot Time
Speeding Up Vista Boot Time :
Found this little gem while looking for something else... thought I'd share it.
When you have a computer with a recent model CPU, chances are it's a dual-core CPU. Both Intel & AMD have been producing dual core CPU's for a few years now. By default, Windows Vista will only use a single core during boot-up. You can easily change this from the System Configuration utility:
1. In Vista's Start Search type msconfig & hit the [Enter] key on your keyboard
2. Once System Configuration has started, select the Boot tab and click the Advanced Options button
2. Once System Configuration has started, select the Boot tab and click the Advanced Options button
3. In the BOOT Advanced Options dialog, check the "Number of processors" check box, and choose 2 (or 4 if you have quad core) for the number of processors.

4. Click OK twice. Done and done.
This should help...
Bandwidth Explained
This is well written explanation about bandwidth, very useful info.
BandWidth Explained
Most hosting companies offer a variety of bandwidth options in their plans. So exactly what is bandwidth as it relates to web hosting? Put simply, bandwidth is the amount of traffic that is allowed to occur between your web site and the rest of the internet. The amount of bandwidth a hosting company can provide is determined by their network connections, both internal to their data center and external to the public internet.
Network Connectivity
The internet, in the most simplest of terms, is a group of millions of computers connected by networks. These connections within the internet can be large or small depending upon the cabling and equipment that is used at a particular internet location. It is the size of each network connection that determines how much bandwidth is available. For example, if you use a DSL connection to connect to the internet, you have 1.54 Mega bits (Mb) of bandwidth. Bandwidth therefore is measured in bits (a single 0 or 1). Bits are grouped in bytes which form words, text, and other information that is transferred between your computer and the internet.
If you have a DSL connection to the internet, you have dedicated bandwidth between your computer and your internet provider. But your internet provider may have thousands of DSL connections to their location. All of these connection aggregate at your internet provider who then has their own dedicated connection to the internet (or multiple connections) which is much larger than your single connection. They must have enough bandwidth to serve your computing needs as well as all of their other customers. So while you have a 1.54Mb connection to your internet provider, your internet provider may have a 255Mb connection to the internet so it can accommodate your needs and up to 166 other users (255/1.54).
Traffic
A very simple analogy to use to understand bandwidth and traffic is to think of highways and cars. Bandwidth is the number of lanes on the highway and traffic is the number of cars on the highway. If you are the only car on a highway, you can travel very quickly. If you are stuck in the middle of rush hour, you may travel very slowly since all of the lanes are being used up.
Traffic is simply the number of bits that are transferred on network connections. It is easiest to understand traffic using examples. One Gigabyte is 2 to the 30th power (1,073,741,824) bytes. One gigabyte is equal to 1,024 megabytes. To put this in perspective, it takes one byte to store one character. Imagine 100 file cabinets in a building, each of these cabinets holds 1000 folders. Each folder has 100 papers. Each paper contains 100 characters - A GB is all the characters in the building. An MP3 song is about 4MB, the same song in wav format is about 40MB, a full length movie can be 800MB to 1000MB (1000MB = 1GB).
If you were to transfer this MP3 song from a web site to your computer, you would create 4MB of traffic between the web site you are downloading from and your computer. Depending upon the network connection between the web site and the internet, the transfer may occur very quickly, or it could take time if other people are also downloading files at the same time. If, for example, the web site you download from has a 10MB connection to the internet, and you are the only person accessing that web site to download your MP3, your 4MB file will be the only traffic on that web site. However, if three people are all downloading that same MP at the same time, 12MB (3 x 4MB) of traffic has been created. Because in this example, the host only has 10MB of bandwidth, someone will have to wait. The network equipment at the hosting company will cycle through each person downloading the file and transfer a small portion at a time so each person's file transfer can take place, but the transfer for everyone downloading the file will be slower. If 100 people all came to the site and downloaded the MP3 at the same time, the transfers would be extremely slow. If the host wanted to decrease the time it took to download files simultaneously, it could increase the bandwidth of their internet connection (at a cost due to upgrading equipment).
Hosting Bandwidth
In the example above, we discussed traffic in terms of downloading an MP3 file. However, each time you visit a web site, you are creating traffic, because in order to view that web page on your computer, the web page is first downloaded to your computer (between the web site and you) which is then displayed using your browser software (Internet Explorer, Netscape, etc.) . The page itself is simply a file that creates traffic just like the MP3 file in the example above (however, a web page is usually much smaller than a music file).
A web page may be very small or large depending upon the amount of text and the number and quality of images integrated within the web page. For example, the home page for CNN.com is about 200KB (200 Kilobytes = 200,000 bytes = 1,600,000 bits). This is typically large for a web page. In comparison, Yahoo's home page is about 70KB.
How Much Bandwidth Is Enough?
It depends (don't you hate that answer). But in truth, it does. Since bandwidth is a significant determinant of hosting plan prices, you should take time to determine just how much is right for you. Almost all hosting plans have bandwidth requirements measured in months, so you need to estimate the amount of bandwidth that will be required by your site on a monthly basis
If you do not intend to provide file download capability from your site, the formula for calculating bandwidth is fairly straightforward:
Average Daily Visitors x Average Page Views x Average Page Size x 31 x Fudge Factor
If you intend to allow people to download files from your site, your bandwidth calculation should be:
[(Average Daily Visitors x Average Page Views x Average Page Size) +(Average Daily File Downloads x Average File Size)] x 31 x Fudge Factor
Let us examine each item in the formula:
Average Daily Visitors - The number of people you expect to visit your site, on average, each day. Depending upon how you market your site, this number could be from 1 to 1,000,000.
Average Page Views - On average, the number of web pages you expect a person to view. If you have 50 web pages in your web site, an average person may only view 5 of those pages each time they visit.
Average Page Size - The average size of your web pages, in Kilobytes (KB). If you have already designed your site, you can calculate this directly.
Average Daily File Downloads - The number of downloads you expect to occur on your site. This is a function of the numbers of visitors and how many times a visitor downloads a file, on average, each day.
Average File Size - Average file size of files that are downloadable from your site. Similar to your web pages, if you already know which files can be downloaded, you can calculate this directly.
Fudge Factor - A number greater than 1. Using 1.5 would be safe, which assumes that your estimate is off by 50%. However, if you were very unsure, you could use 2 or 3 to ensure that your bandwidth requirements are more than met.
Usually, hosting plans offer bandwidth in terms of Gigabytes (GB) per month. This is why our formula takes daily averages and multiplies them by 31.
Summary
Most personal or small business sites will not need more than 1GB of bandwidth per month. If you have a web site that is composed of static web pages and you expect little traffic to your site on a daily basis, go with a low bandwidth plan. If you go over the amount of bandwidth allocated in your plan, your hosting company could charge you over usage fees, so if you think the traffic to your site will be significant, you may want to go through the calculations above to estimate the amount of bandwidth required in a hosting plan.
__________________
BandWidth Explained
Most hosting companies offer a variety of bandwidth options in their plans. So exactly what is bandwidth as it relates to web hosting? Put simply, bandwidth is the amount of traffic that is allowed to occur between your web site and the rest of the internet. The amount of bandwidth a hosting company can provide is determined by their network connections, both internal to their data center and external to the public internet.
Network Connectivity
The internet, in the most simplest of terms, is a group of millions of computers connected by networks. These connections within the internet can be large or small depending upon the cabling and equipment that is used at a particular internet location. It is the size of each network connection that determines how much bandwidth is available. For example, if you use a DSL connection to connect to the internet, you have 1.54 Mega bits (Mb) of bandwidth. Bandwidth therefore is measured in bits (a single 0 or 1). Bits are grouped in bytes which form words, text, and other information that is transferred between your computer and the internet.
If you have a DSL connection to the internet, you have dedicated bandwidth between your computer and your internet provider. But your internet provider may have thousands of DSL connections to their location. All of these connection aggregate at your internet provider who then has their own dedicated connection to the internet (or multiple connections) which is much larger than your single connection. They must have enough bandwidth to serve your computing needs as well as all of their other customers. So while you have a 1.54Mb connection to your internet provider, your internet provider may have a 255Mb connection to the internet so it can accommodate your needs and up to 166 other users (255/1.54).
Traffic
A very simple analogy to use to understand bandwidth and traffic is to think of highways and cars. Bandwidth is the number of lanes on the highway and traffic is the number of cars on the highway. If you are the only car on a highway, you can travel very quickly. If you are stuck in the middle of rush hour, you may travel very slowly since all of the lanes are being used up.
Traffic is simply the number of bits that are transferred on network connections. It is easiest to understand traffic using examples. One Gigabyte is 2 to the 30th power (1,073,741,824) bytes. One gigabyte is equal to 1,024 megabytes. To put this in perspective, it takes one byte to store one character. Imagine 100 file cabinets in a building, each of these cabinets holds 1000 folders. Each folder has 100 papers. Each paper contains 100 characters - A GB is all the characters in the building. An MP3 song is about 4MB, the same song in wav format is about 40MB, a full length movie can be 800MB to 1000MB (1000MB = 1GB).
If you were to transfer this MP3 song from a web site to your computer, you would create 4MB of traffic between the web site you are downloading from and your computer. Depending upon the network connection between the web site and the internet, the transfer may occur very quickly, or it could take time if other people are also downloading files at the same time. If, for example, the web site you download from has a 10MB connection to the internet, and you are the only person accessing that web site to download your MP3, your 4MB file will be the only traffic on that web site. However, if three people are all downloading that same MP at the same time, 12MB (3 x 4MB) of traffic has been created. Because in this example, the host only has 10MB of bandwidth, someone will have to wait. The network equipment at the hosting company will cycle through each person downloading the file and transfer a small portion at a time so each person's file transfer can take place, but the transfer for everyone downloading the file will be slower. If 100 people all came to the site and downloaded the MP3 at the same time, the transfers would be extremely slow. If the host wanted to decrease the time it took to download files simultaneously, it could increase the bandwidth of their internet connection (at a cost due to upgrading equipment).
Hosting Bandwidth
In the example above, we discussed traffic in terms of downloading an MP3 file. However, each time you visit a web site, you are creating traffic, because in order to view that web page on your computer, the web page is first downloaded to your computer (between the web site and you) which is then displayed using your browser software (Internet Explorer, Netscape, etc.) . The page itself is simply a file that creates traffic just like the MP3 file in the example above (however, a web page is usually much smaller than a music file).
A web page may be very small or large depending upon the amount of text and the number and quality of images integrated within the web page. For example, the home page for CNN.com is about 200KB (200 Kilobytes = 200,000 bytes = 1,600,000 bits). This is typically large for a web page. In comparison, Yahoo's home page is about 70KB.
How Much Bandwidth Is Enough?
It depends (don't you hate that answer). But in truth, it does. Since bandwidth is a significant determinant of hosting plan prices, you should take time to determine just how much is right for you. Almost all hosting plans have bandwidth requirements measured in months, so you need to estimate the amount of bandwidth that will be required by your site on a monthly basis
If you do not intend to provide file download capability from your site, the formula for calculating bandwidth is fairly straightforward:
Average Daily Visitors x Average Page Views x Average Page Size x 31 x Fudge Factor
If you intend to allow people to download files from your site, your bandwidth calculation should be:
[(Average Daily Visitors x Average Page Views x Average Page Size) +(Average Daily File Downloads x Average File Size)] x 31 x Fudge Factor
Let us examine each item in the formula:
Average Daily Visitors - The number of people you expect to visit your site, on average, each day. Depending upon how you market your site, this number could be from 1 to 1,000,000.
Average Page Views - On average, the number of web pages you expect a person to view. If you have 50 web pages in your web site, an average person may only view 5 of those pages each time they visit.
Average Page Size - The average size of your web pages, in Kilobytes (KB). If you have already designed your site, you can calculate this directly.
Average Daily File Downloads - The number of downloads you expect to occur on your site. This is a function of the numbers of visitors and how many times a visitor downloads a file, on average, each day.
Average File Size - Average file size of files that are downloadable from your site. Similar to your web pages, if you already know which files can be downloaded, you can calculate this directly.
Fudge Factor - A number greater than 1. Using 1.5 would be safe, which assumes that your estimate is off by 50%. However, if you were very unsure, you could use 2 or 3 to ensure that your bandwidth requirements are more than met.
Usually, hosting plans offer bandwidth in terms of Gigabytes (GB) per month. This is why our formula takes daily averages and multiplies them by 31.
Summary
Most personal or small business sites will not need more than 1GB of bandwidth per month. If you have a web site that is composed of static web pages and you expect little traffic to your site on a daily basis, go with a low bandwidth plan. If you go over the amount of bandwidth allocated in your plan, your hosting company could charge you over usage fees, so if you think the traffic to your site will be significant, you may want to go through the calculations above to estimate the amount of bandwidth required in a hosting plan.
__________________
Saturday, March 15, 2008
How To Find WINDOWS XP CD-KEY in 10 seconds
How To Find WINDOWS XP CD-KEY in 10 seconds
insert your xp cd
browse to the i386 folder
find and open unattended.txt
scroll down to see the cd-key
insert your xp cd
browse to the i386 folder
find and open unattended.txt
scroll down to see the cd-key
Do have an anti-virus program.
Do have an anti-virus program.
How can you test that it works?
This is a good question and it is wise to familiarize yourself with how your anti-virus software behaves when it detects a virus, before it really happens. One quick way to do this is to use the EICAR Anti-Virus Test File. This is a test file that will cause no damage to your system and still allow you to test if anti-virus tool is awake.Here are some steps:
1. Open a text editor (e.g. Notepad)
2. Enter the following text in it:
X5O!P%@AP[4\PZX54(P^)7CC)7}$EICAR-STANDARD-ANTIVIRUS-TEST-FILE!$H+H*
3. Save the file as EICAR.COM on your desktop.
4. Open DOS and try to execute this .COM file (or simply double-click the file on Desktop)If your anti-virus software is working properly, it will warn you that a virus has been detected when you attempt to run the .COM file.
To be double-sure, zip this file, and then try double-clicking on the ZIP file to see if your AV tool recognized viruses inside ZIP files.
You can also send this file to yourself as an attachment, just to verify if your AV tool has command of email cleanliness.
This works...
How can you test that it works?
This is a good question and it is wise to familiarize yourself with how your anti-virus software behaves when it detects a virus, before it really happens. One quick way to do this is to use the EICAR Anti-Virus Test File. This is a test file that will cause no damage to your system and still allow you to test if anti-virus tool is awake.Here are some steps:
1. Open a text editor (e.g. Notepad)
2. Enter the following text in it:
X5O!P%@AP[4\PZX54(P^)7CC)7}$EICAR-STANDARD-ANTIVIRUS-TEST-FILE!$H+H*
3. Save the file as EICAR.COM on your desktop.
4. Open DOS and try to execute this .COM file (or simply double-click the file on Desktop)If your anti-virus software is working properly, it will warn you that a virus has been detected when you attempt to run the .COM file.
To be double-sure, zip this file, and then try double-clicking on the ZIP file to see if your AV tool recognized viruses inside ZIP files.
You can also send this file to yourself as an attachment, just to verify if your AV tool has command of email cleanliness.
This works...
Tuesday, January 29, 2008
Change Default Wallpaper Folder to My Pictures on Windows XP
Change Default Wallpaper Folder to My Pictures on Windows XP
Have you ever wondered why Windows XP had such terribly ugly wallpapers to choose from? On top of that, there's no way to easily change the list of backgrounds to a folder you might actually use… like your My Pictures folder.
There's a fairly simple registry hack you can do to make Windows look in a different folder, but if you want to get rid of Blue Lace 16 you'll also have to delete it manually. (The standard warnings about registry editing apply here)
Change Wallpaper Folder
Open up regedit.exe using the start menu Run box, and then navigate down to the following key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\Curr entVersion
On the right-hand side you should see a value called WallPaperDir, which defines the folder Windows uses to populate the list. If the key does not exist, then you can create a new string value with the same name.
Double-click to change the value, and then paste in the full path to your My Pictures folder. (Note that you could specify any path here if you wanted to.)
The change should be immediate, the next time you open the Desktop panel… but you'll notice a number of default images still in the list. Turns out that Windows also queries the Windows folder for images…
To get rid of those, browse to C:\Windows and then look for a set of horribly ugly Bitmap files
You can delete these images to make them stop appearing in the wallpaper selection list, just be careful not to delete anything else in your Windows folder or you likely won't be able to boot anymore.
Another annoyance solved…
Have you ever wondered why Windows XP had such terribly ugly wallpapers to choose from? On top of that, there's no way to easily change the list of backgrounds to a folder you might actually use… like your My Pictures folder.
There's a fairly simple registry hack you can do to make Windows look in a different folder, but if you want to get rid of Blue Lace 16 you'll also have to delete it manually. (The standard warnings about registry editing apply here)
Change Wallpaper Folder
Open up regedit.exe using the start menu Run box, and then navigate down to the following key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\Curr entVersion
On the right-hand side you should see a value called WallPaperDir, which defines the folder Windows uses to populate the list. If the key does not exist, then you can create a new string value with the same name.
Double-click to change the value, and then paste in the full path to your My Pictures folder. (Note that you could specify any path here if you wanted to.)
The change should be immediate, the next time you open the Desktop panel… but you'll notice a number of default images still in the list. Turns out that Windows also queries the Windows folder for images…
To get rid of those, browse to C:\Windows and then look for a set of horribly ugly Bitmap files
You can delete these images to make them stop appearing in the wallpaper selection list, just be careful not to delete anything else in your Windows folder or you likely won't be able to boot anymore.
Another annoyance solved…
Thursday, January 24, 2008
What is svchost.exe And Why Is It Running?
What is svchost.exe And Why Is It Running?
According to Microsoft: "svchost.exe is a generic host process name for services that run from dynamic-link libraries". Could we have that in english please?
Some time ago, Microsoft started moving all of the functionality from internal Windows services into .dll files instead of .exe files. From a programming perspective this makes more sense for reusability… but the problem is that you can't launch a .dll file directly from Windows, it has to be loaded up from a running executable (.exe). Thus the svchost.exe process was born.
Why Are There So Many svchost.exes Running?
If you've ever taken a look at the Services section in control panel you might notice that there are a Lot of services required by Windows. If every single service ran under a single svchost.exe instance, a failure in one might bring down all of Windows… so they are separated out.
Those services are organized into logical groups, and then a single svchost.exe instance is created for each group. For instance, one svchost.exe instance runs the 3 services related to the firewall. Another svchost.exe instance might run all the services related to the user interface, and so on.
You can trim down unneeded services by disabling or stopping the services that don't absolutely need to be running. Additionally, if you are noticing very heavy CPU usage on a single svchost.exe instance you can restart the services running under that instance.
The biggest problem is identifying what services are being run on a particular svchost.exe instance… we'll cover that below.
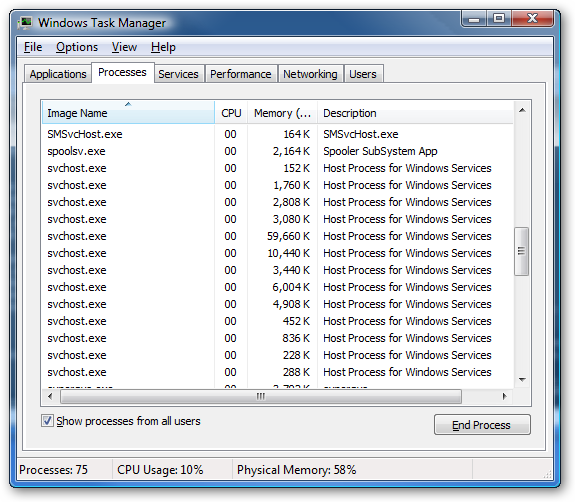
If you are curious what we're talking about, just open up Task Manager and check the "Show processes from all users" box:
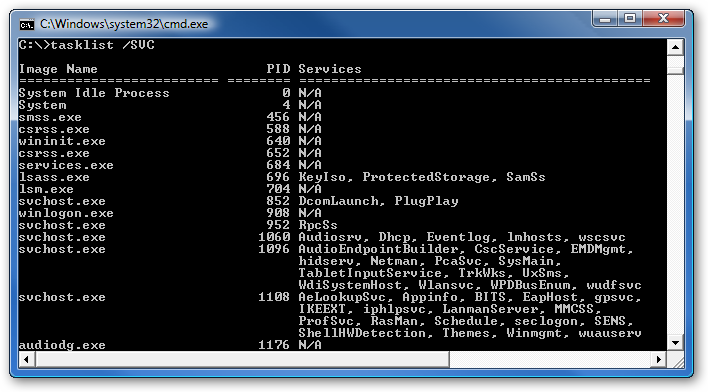
If you want to see what services are being hosted by a particular svchost.exe instance, you can use the tasklist command from the command prompt in order to see the list of services.
type: tasklist /SVC
Checking in Task Manager in Vista
Using Process Explorer in Vista or XP
Hopefully this helps somebody!
You are no doubt reading this article because you are wondering why on earth there are nearly a dozen processes running with the name svchost.exe. You can't kill them, and you don't remember starting them… so what are they?
So What Is It?
According to Microsoft: "svchost.exe is a generic host process name for services that run from dynamic-link libraries". Could we have that in english please?
Some time ago, Microsoft started moving all of the functionality from internal Windows services into .dll files instead of .exe files. From a programming perspective this makes more sense for reusability… but the problem is that you can't launch a .dll file directly from Windows, it has to be loaded up from a running executable (.exe). Thus the svchost.exe process was born.
Why Are There So Many svchost.exes Running?
If you've ever taken a look at the Services section in control panel you might notice that there are a Lot of services required by Windows. If every single service ran under a single svchost.exe instance, a failure in one might bring down all of Windows… so they are separated out.
Those services are organized into logical groups, and then a single svchost.exe instance is created for each group. For instance, one svchost.exe instance runs the 3 services related to the firewall. Another svchost.exe instance might run all the services related to the user interface, and so on.
So What Can I Do About It?
You can trim down unneeded services by disabling or stopping the services that don't absolutely need to be running. Additionally, if you are noticing very heavy CPU usage on a single svchost.exe instance you can restart the services running under that instance.
The biggest problem is identifying what services are being run on a particular svchost.exe instance… we'll cover that below.
If you are curious what we're talking about, just open up Task Manager and check the "Show processes from all users" box:
Checking From the Command Line (Vista or XP)
If you want to see what services are being hosted by a particular svchost.exe instance, you can use the tasklist command from the command prompt in order to see the list of services.
type: tasklist /SVC
The problem with using the command line method is that you don't necessarily know what these cryptic names refer to.
Checking in Task Manager in Vista
You can right-click on a particular svchost.exe process, and then choose the "Go to Service" option.
This will flip over to the Services tab, where the services running under that svchost.exe process will be selected:
The great thing about doing it this way is that you can see the real name under the Description column, so you can choose to disable the service if you don't want it running.
Using Process Explorer in Vista or XP
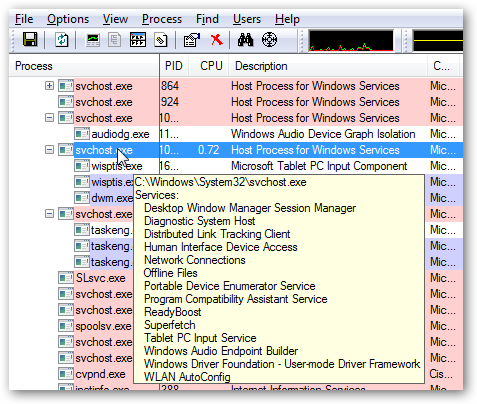
You can use the excellent Process Explorer utility from Microsoft/Sysinternals to see what services are running as a part of a svchost.exe process.
Hovering your mouse over one of the processes will show you a popup list of all the services:
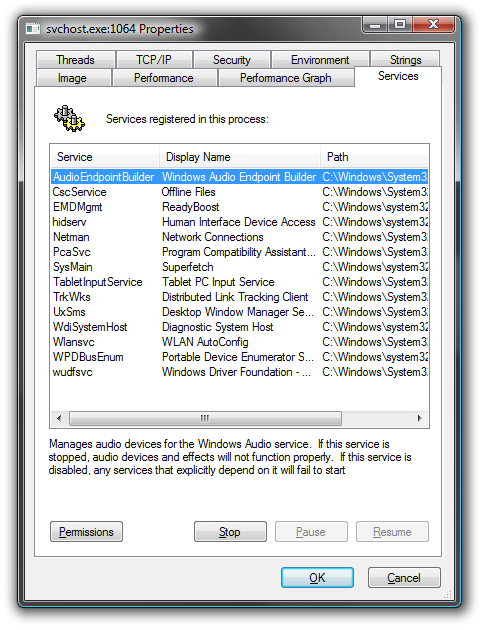
Or you can double-click on a svchost.exe instance and select the Services tab, where you can choose to stop one of the services if you choose.
Disabling Services
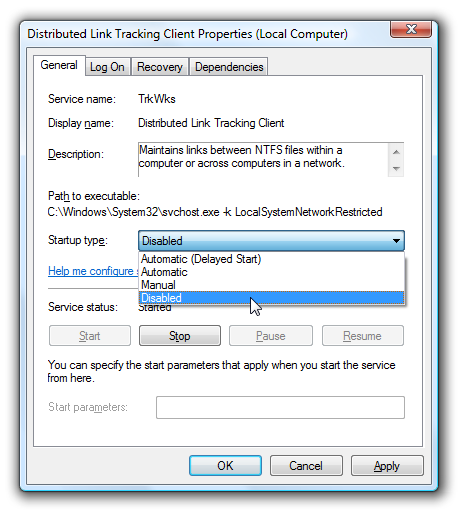
Open up Services from the administrative tools section of Control Panel, or type services.msc into the start menu search or run box.
Find the service in the list that you'd like to disable, and either double-click on it or right-click and choose Properties.
Change the Startup Type to Disabled, and then click the Stop button to immediately stop it.
You could also use the command prompt to disable the service if you choose. In this command "trkwks" is the Service name from the above dialog, but if you go back to the tasklist command at the beginning of this article you'll notice you can find it there as well.
sc config trkwks start= disabled
Hopefully this helps somebody!
Courtesy: how to geek
Monday, January 21, 2008
Enabling right click on sites that disable it
Enabling right click on sites that disable it
Enabling right click on sites that disable itLots of web sites have disabled the right click function of the mouse button... it's really, really annoying. This is done so that you don't steal (via right-click->save picture) their photos or images or any other goodies. Unfortunately, it disables ALL right-click functionality: copy, paste, open in new window.
INTERNET EXPLORER
It's easy to change, assuming your using IE 6:
Click "Tools"->"Internet Options"
Click the "Security" tab
Click "Custom Level"
Scroll down to the "Scripting" section
Set "Active Scripting" to "disable"
Click "Ok" a couple of times.
You'll probably want to turn this back to "enable" when your done... 'cause generally the javascript enhances a website.
Mozilla Firefox
1. Go to Tools tools> Options and select Web Options from the left panel.
2. You would see that Enable Javascript is checked by default. Uncheck it and click OK.
3. Right Clicking should now be enabled on websites that do not allow it.
4. If this does not work, you could disable java altogether from the check box in the same window.
Opera
1. Go to ->Tools “>Preferences and select the Advanced"Tab.
2. From the left panel, select "Content"
3. You would see that Enable Javascript is checked by default. Uncheck it and click OK.
4. Right Clicking should now be enabled on websites that do not allow it.
5. If this does not work, you could disable java altogether.
Enjoy...
Enabling right click on sites that disable itLots of web sites have disabled the right click function of the mouse button... it's really, really annoying. This is done so that you don't steal (via right-click->save picture) their photos or images or any other goodies. Unfortunately, it disables ALL right-click functionality: copy, paste, open in new window.
INTERNET EXPLORER
It's easy to change, assuming your using IE 6:
Click "Tools"->"Internet Options"
Click the "Security" tab
Click "Custom Level"
Scroll down to the "Scripting" section
Set "Active Scripting" to "disable"
Click "Ok" a couple of times.
You'll probably want to turn this back to "enable" when your done... 'cause generally the javascript enhances a website.
Mozilla Firefox
1. Go to Tools tools> Options and select Web Options from the left panel.
2. You would see that Enable Javascript is checked by default. Uncheck it and click OK.
3. Right Clicking should now be enabled on websites that do not allow it.
4. If this does not work, you could disable java altogether from the check box in the same window.
Opera
1. Go to ->Tools “>Preferences and select the Advanced"Tab.
2. From the left panel, select "Content"
3. You would see that Enable Javascript is checked by default. Uncheck it and click OK.
4. Right Clicking should now be enabled on websites that do not allow it.
5. If this does not work, you could disable java altogether.
Enjoy...
Tuesday, January 15, 2008
Boot Your PC in Style
Boot Your PC in Style
Note : I recommend making a copy of you "Boot.ini" first, just in case you do something wrong and your window is not booting, restart and when your pc is in post(the black screen) press F8 and boot in safe mode, and replace the "Boot.ini" with your backup of "Boot.ini" and it should get back to its former state.
All of us are accustomed to seeing the Windows XP logo at system startupbut how about getting a custom message at first before the logo appears?
Heres how to do it. Its easy and simple.
Please don't mess it up until n unless you're DUMB enough.
Click start,then run.
Type c:\boot.ini
Erase whatever is there and copy and paste this
[boot loader]
timeout=5
default=multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)\WINDOWS
[operating systems]
multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)\WINDOWS="Write your message"/fastdetect
C:\="write your message"
Write whatever you want in between the quotes this will display for 5 seconds before windows starts
*if you have installed windows in any partition other than C:
replace the number after the last brackets of multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)
Use1 for c:\
2 for d:\ and
so onIf you want to create more lines just writed:\="......"e:\="....."
After editing the file "Boot.ini" save it and restart the system to see how it goes.
Sample:
[boot loader]
timeout=10
default=multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)\WINDOW S
[operating systems]multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)\WINDOWS="This PC will blow in"/fastdetect
C:\="10 seconds"
D:\="Shut it down"
E:\="Or run for your LIFE"
Try it and next time when friends comes to see your PC I bet they will be astonished
Note : I recommend making a copy of you "Boot.ini" first, just in case you do something wrong and your window is not booting, restart and when your pc is in post(the black screen) press F8 and boot in safe mode, and replace the "Boot.ini" with your backup of "Boot.ini" and it should get back to its former state.
All of us are accustomed to seeing the Windows XP logo at system startupbut how about getting a custom message at first before the logo appears?
Heres how to do it. Its easy and simple.
Please don't mess it up until n unless you're DUMB enough.
Click start,then run.
Type c:\boot.ini
Erase whatever is there and copy and paste this
[boot loader]
timeout=5
default=multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)\WINDOWS
[operating systems]
multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)\WINDOWS="Write your message"/fastdetect
C:\="write your message"
Write whatever you want in between the quotes this will display for 5 seconds before windows starts
*if you have installed windows in any partition other than C:
replace the number after the last brackets of multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)
Use1 for c:\
2 for d:\ and
so onIf you want to create more lines just writed:\="......"e:\="....."
After editing the file "Boot.ini" save it and restart the system to see how it goes.
Sample:
[boot loader]
timeout=10
default=multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)\WINDOW S
[operating systems]multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)\WINDOWS="This PC will blow in"/fastdetect
C:\="10 seconds"
D:\="Shut it down"
E:\="Or run for your LIFE"
Try it and next time when friends comes to see your PC I bet they will be astonished
Add Internet URL address bar to your Windows XP Taskbar
Add Internet URL address bar to your Windows XP Taskbar
You can add an Internet URL address bar to your Windows XP taskbar. Doing so will let you type in URLs and launch Web pages without first launching a browser. It will also let you launch some native Windows XP applications in much the same way as you would via the Run menu (so you could type in calc to launch the calculator or mspaint to launch Microsoft Paint. Here's how you add the address bar:
1. Right-click on the taskbar, select Toolbars, and then click Address.
2. The word Address will appear on your taskbar.
3. Double click it to access it.
4. If that doesn't work, your taskbar is locked. You can unlock it by right-clicking on the taskbar again and uncheck Lock the Taskbar.
NOTE: You may also need to grab the vertical dotted lines beside the word Address and drag it to the left to make the Address window appear.
You can add an Internet URL address bar to your Windows XP taskbar. Doing so will let you type in URLs and launch Web pages without first launching a browser. It will also let you launch some native Windows XP applications in much the same way as you would via the Run menu (so you could type in calc to launch the calculator or mspaint to launch Microsoft Paint. Here's how you add the address bar:
1. Right-click on the taskbar, select Toolbars, and then click Address.
2. The word Address will appear on your taskbar.
3. Double click it to access it.
4. If that doesn't work, your taskbar is locked. You can unlock it by right-clicking on the taskbar again and uncheck Lock the Taskbar.
NOTE: You may also need to grab the vertical dotted lines beside the word Address and drag it to the left to make the Address window appear.
Change Default Location for Installing Applications
Change Default Location for Installing Applications
Windows XP uses the C:\Program Files directory as the default base directory into which new programs are installed.
However, you can change the default installation drive and/ or directory by using a Registry hack.
Run the Registry Editor (regedit)and go to
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\Curr entVersion
Look for the value named ProgramFilesDir. by default,this value will be C:\Program Files.
Edit the value to any valid drive or folder and XP will use that new location as the default installation directory for new programs.
Windows XP uses the C:\Program Files directory as the default base directory into which new programs are installed.
However, you can change the default installation drive and/ or directory by using a Registry hack.
Run the Registry Editor (regedit)and go to
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\Curr entVersion
Look for the value named ProgramFilesDir. by default,this value will be C:\Program Files.
Edit the value to any valid drive or folder and XP will use that new location as the default installation directory for new programs.
Saturday, January 5, 2008
13 of the Best Ways to Speed up your PC
13 of the Best Ways to Speed up your PC
Say that you wake up and want to check the traffic before you head out the door. You turn on your computer and wait. And wait. Finally you give up and decide to make some coffee, toast a bagel, and maybe grab the newspaper and check out the crossword puzzle. By the time you finally return, your computer has just completed its leisurely start up. Sound a little too familiar? While a complete computer overhaul might not be too far off, there are a few things that you can do in the meantime if a new computer isn’t in your budget. Here are a few tips for giving your computer a speed boost.
Defragment: If your computer is running slowly it may be because your files are scattered all over your hard drive. When you save a file on your computer it goes to the first available space on your hard drive. When that gets filled up it stores other parts of your file in the next available place, then the next place, and so on. When files become fragmented like this, the computer has to spend time searching the hard drive to piece them back together. This process slows you and your system down. Luckily, this is a fairly easy fix. Simply follow these steps: For a PC, go to Start menu and open your Programs menu. From there go to Accessories then Program Tools. You should see the icon for the Disk Defragmentation program in that menu. Simply click on it and windows will begin the defrag process. Be advised, however, that this process usually takes a long time so it could be something you set up to run before you go to bed or before you go to work in the morning.
Clean Up Registry: Not everyone agrees that a PC registry clean-up is much of a help, but it can’t hurt to try if you’re frustrated with your computer speed. Before you do anything to your registry, however, make sure you have it backed up as making changes to the registry can have big affects on how your computer runs. Don’t delete things from the registry when you are unsure of the function, as it can wreck havoc on your computer. Be cautious and try to use a free registry-cleaning program like CCleaner, which will not only clean out your registry but it will take care of several of some other issues listed here as well.
Remove Old Programs: Have things installed on your computer that you haven’t used in ages? Do you even know what’s installed on your computer? It’s possible all these old programs could clog up your hard drive and slow your computer down. Go to your Start menu and select the Control Panel and then Add or Remove programs. It will bring up a list of all the programs that are installed on your computer and also tell you how often you use them. If the answer is “never,” you can most likely safely uninstall the programs and free up valuable space.
Keep Spyware in Check: Spyware seems to be almost unavoidable these days for anyone who uses the Internet. Virus protection programs often catch the worst culprits but there is always something that sneaks through, and these culprits can slow your computer down. If you think you might have a spyware infection, or if you just want to be on the safe side, you can use a free program like AdAware to check your computer for spyware.
Repair Disk Errors: While defragmentation might take care of the worst of your disk problems, you can also be slowed down by errors in other places on your disk drive. As you store and delete files on your hard drive, bad sectors can develop. These sectors can make accessing or saving files difficult and they can slow your computer down. You can check for problems by running another Windows utility. Go to your Start menu and click on My Computer. When the My Computer window comes up right click on the drive you want to check for errors. When the drop down menu shows up go to properties. This will bring a box up and you’ll click on Tools. Check the box that says scan and attempt recovery of bad sectors then click start. Once this is done you’ll be given the option to fix the bad sectors, and you’ll want to select “yes.” Fixing any bad areas in your drives can add some significant speed to your system.
Get Rid of Temporary Files: Windows is notorious for storing temporary files that can clog up your hard drive and slow down your computer. These temporary files aren’t going to go anywhere unless you ask them to, and that’s where the disk cleanup tool can come in handy. To run an automatic disk cleanup just go to Programs under your Start menu. It’s under Accessories and then System Tools. There you should see the icon for disk cleanup. You’ll simply need to run the cleanup program and it will determine what you can safely get rid of on your computer (this will usually be just temporary files and things you’ve yet to empty from the recycle bin). You’d be surprised how much room you can free up by eliminating these files.
Clean Up Your Desktop: Some of you, and you know who you are, have virtual desktops that are just as messy as your real desktops. This may not seem like a big deal, but it’s important enough that windows will give you little nudging reminders to clean up your desktop (which, if you’re like me, you promptly ignore). Go through all the stuff you have on your desktop, delete the shortcuts you no longer use, and organize all the remaining miscellaneous files.
Clear your Inbox:If you’re using Outlook or Outlook Express as your email client you might want to check to see just how many old emails you have hanging around. These could be clogging up your memory and causing your computer to run more slowly than it should. If you haven’t checked that spam folder it could chock full of computer-clogging waste. Go through your old emails and weed out those emails that you might not actually need.
Reinstall Windows: If you’re getting desperate for a computer fix, and if you have the time to spend, a Windows reinstall can be one option to speed up your system. Make absolutely sure you’ve backed up any data that’s important to you before you begin, otherwise those files be lost. Then you can begin to wipe the slate clean, reformat your hard drive, reinstall your applications, and put your files back onto your computer from the backup. You’ll be eliminating years of junk that can slow down your system. The basic reinstallation is fairly simple if you use the recovery disk that came with your computer; but reinstalling all your applications can take a long time, so be prepared.
Check for Viruses: You can never be quite sure what is lurking on your computer, so make sure your anti-virus program has the latest updates, and run a full scan of your computer. Virus programs can often disguise themselves as legitimate windows applications so they can be hiding out in places you might not have noticed. If you don’t have an anti-virus program (shame on you!) you can try a free one like Avast!.
Stop Unnecessary Services: Often when you install a new program it will add itself to the programs that start automatically when your computer boots up. All of these unnecessary programs can slow down your startup. You can disable these programs by going to the start menu and then click on Run. Type “msconfig” in the box that comes up. Click on the Startup tab and you’ll be able to see all the pesky programs that bog down your startup time. Get rid of anything that doesn’t look absolutely necessary, but be careful to avoid any Windows system components.
Install Updates: Keeping your computers operating system and drivers up to date is very important in maintaining performance. Updates also help make your computer more secure and reliable, improving performance indirectly as well. Most Windows updates can be downloaded from the Internet and installed (mine does this automatically) but you can use the Windows Update site to gain access to the updates as well. This site is accessible only if you’re running Internet Explorer (IE).
Delete Old Network Connections: Another thing to check that might slow your computer down is old network connections. Your computer will waste time searching for old drives and ports that no longer exist. You can delete these connections by going into your control panel and selecting Network Connections. You should find a list of all the networks your computer recognizes, and you can delete those that are no longer necessary.
Technology is supposed to make your life easier, not more irritating. Hopefully, some of these tips will help you shave at least a few minutes off the time it takes for your computer to get going, whether just starting up or when you try to run a program (or multiple programs). But, if you’d tried all of these tips and your computer still refuses to kick it up a notch, it might be time to send it to the computer heaven. But don’t give up without a fight without trying all of these tips.
Unlike a new computer purchase, these tips are free, so you’ve got nothing to lose.But, if it’s time for a new computer, be smart about how you purchase one. Look for deals where you can pay over time with no interest, or use a card that has 0% APR. Then sock that monthly payment away in a savings account until it comes due. You’ll save a little money on this high-ticket item, and you’ll have a tax write-off if you use it for business. Keep this list of tips around, and you may never have a slow-down problem with your new computer!
Say that you wake up and want to check the traffic before you head out the door. You turn on your computer and wait. And wait. Finally you give up and decide to make some coffee, toast a bagel, and maybe grab the newspaper and check out the crossword puzzle. By the time you finally return, your computer has just completed its leisurely start up. Sound a little too familiar? While a complete computer overhaul might not be too far off, there are a few things that you can do in the meantime if a new computer isn’t in your budget. Here are a few tips for giving your computer a speed boost.
Defragment: If your computer is running slowly it may be because your files are scattered all over your hard drive. When you save a file on your computer it goes to the first available space on your hard drive. When that gets filled up it stores other parts of your file in the next available place, then the next place, and so on. When files become fragmented like this, the computer has to spend time searching the hard drive to piece them back together. This process slows you and your system down. Luckily, this is a fairly easy fix. Simply follow these steps: For a PC, go to Start menu and open your Programs menu. From there go to Accessories then Program Tools. You should see the icon for the Disk Defragmentation program in that menu. Simply click on it and windows will begin the defrag process. Be advised, however, that this process usually takes a long time so it could be something you set up to run before you go to bed or before you go to work in the morning.
Clean Up Registry: Not everyone agrees that a PC registry clean-up is much of a help, but it can’t hurt to try if you’re frustrated with your computer speed. Before you do anything to your registry, however, make sure you have it backed up as making changes to the registry can have big affects on how your computer runs. Don’t delete things from the registry when you are unsure of the function, as it can wreck havoc on your computer. Be cautious and try to use a free registry-cleaning program like CCleaner, which will not only clean out your registry but it will take care of several of some other issues listed here as well.
Remove Old Programs: Have things installed on your computer that you haven’t used in ages? Do you even know what’s installed on your computer? It’s possible all these old programs could clog up your hard drive and slow your computer down. Go to your Start menu and select the Control Panel and then Add or Remove programs. It will bring up a list of all the programs that are installed on your computer and also tell you how often you use them. If the answer is “never,” you can most likely safely uninstall the programs and free up valuable space.
Keep Spyware in Check: Spyware seems to be almost unavoidable these days for anyone who uses the Internet. Virus protection programs often catch the worst culprits but there is always something that sneaks through, and these culprits can slow your computer down. If you think you might have a spyware infection, or if you just want to be on the safe side, you can use a free program like AdAware to check your computer for spyware.
Repair Disk Errors: While defragmentation might take care of the worst of your disk problems, you can also be slowed down by errors in other places on your disk drive. As you store and delete files on your hard drive, bad sectors can develop. These sectors can make accessing or saving files difficult and they can slow your computer down. You can check for problems by running another Windows utility. Go to your Start menu and click on My Computer. When the My Computer window comes up right click on the drive you want to check for errors. When the drop down menu shows up go to properties. This will bring a box up and you’ll click on Tools. Check the box that says scan and attempt recovery of bad sectors then click start. Once this is done you’ll be given the option to fix the bad sectors, and you’ll want to select “yes.” Fixing any bad areas in your drives can add some significant speed to your system.
Get Rid of Temporary Files: Windows is notorious for storing temporary files that can clog up your hard drive and slow down your computer. These temporary files aren’t going to go anywhere unless you ask them to, and that’s where the disk cleanup tool can come in handy. To run an automatic disk cleanup just go to Programs under your Start menu. It’s under Accessories and then System Tools. There you should see the icon for disk cleanup. You’ll simply need to run the cleanup program and it will determine what you can safely get rid of on your computer (this will usually be just temporary files and things you’ve yet to empty from the recycle bin). You’d be surprised how much room you can free up by eliminating these files.
Clean Up Your Desktop: Some of you, and you know who you are, have virtual desktops that are just as messy as your real desktops. This may not seem like a big deal, but it’s important enough that windows will give you little nudging reminders to clean up your desktop (which, if you’re like me, you promptly ignore). Go through all the stuff you have on your desktop, delete the shortcuts you no longer use, and organize all the remaining miscellaneous files.
Clear your Inbox:If you’re using Outlook or Outlook Express as your email client you might want to check to see just how many old emails you have hanging around. These could be clogging up your memory and causing your computer to run more slowly than it should. If you haven’t checked that spam folder it could chock full of computer-clogging waste. Go through your old emails and weed out those emails that you might not actually need.
Reinstall Windows: If you’re getting desperate for a computer fix, and if you have the time to spend, a Windows reinstall can be one option to speed up your system. Make absolutely sure you’ve backed up any data that’s important to you before you begin, otherwise those files be lost. Then you can begin to wipe the slate clean, reformat your hard drive, reinstall your applications, and put your files back onto your computer from the backup. You’ll be eliminating years of junk that can slow down your system. The basic reinstallation is fairly simple if you use the recovery disk that came with your computer; but reinstalling all your applications can take a long time, so be prepared.
Check for Viruses: You can never be quite sure what is lurking on your computer, so make sure your anti-virus program has the latest updates, and run a full scan of your computer. Virus programs can often disguise themselves as legitimate windows applications so they can be hiding out in places you might not have noticed. If you don’t have an anti-virus program (shame on you!) you can try a free one like Avast!.
Stop Unnecessary Services: Often when you install a new program it will add itself to the programs that start automatically when your computer boots up. All of these unnecessary programs can slow down your startup. You can disable these programs by going to the start menu and then click on Run. Type “msconfig” in the box that comes up. Click on the Startup tab and you’ll be able to see all the pesky programs that bog down your startup time. Get rid of anything that doesn’t look absolutely necessary, but be careful to avoid any Windows system components.
Install Updates: Keeping your computers operating system and drivers up to date is very important in maintaining performance. Updates also help make your computer more secure and reliable, improving performance indirectly as well. Most Windows updates can be downloaded from the Internet and installed (mine does this automatically) but you can use the Windows Update site to gain access to the updates as well. This site is accessible only if you’re running Internet Explorer (IE).
Delete Old Network Connections: Another thing to check that might slow your computer down is old network connections. Your computer will waste time searching for old drives and ports that no longer exist. You can delete these connections by going into your control panel and selecting Network Connections. You should find a list of all the networks your computer recognizes, and you can delete those that are no longer necessary.
Technology is supposed to make your life easier, not more irritating. Hopefully, some of these tips will help you shave at least a few minutes off the time it takes for your computer to get going, whether just starting up or when you try to run a program (or multiple programs). But, if you’d tried all of these tips and your computer still refuses to kick it up a notch, it might be time to send it to the computer heaven. But don’t give up without a fight without trying all of these tips.
Unlike a new computer purchase, these tips are free, so you’ve got nothing to lose.But, if it’s time for a new computer, be smart about how you purchase one. Look for deals where you can pay over time with no interest, or use a card that has 0% APR. Then sock that monthly payment away in a savings account until it comes due. You’ll save a little money on this high-ticket item, and you’ll have a tax write-off if you use it for business. Keep this list of tips around, and you may never have a slow-down problem with your new computer!
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)